1. Understanding Instructional Design
At its core, instructional design is about designing instructional materials and activities that align with specific learning objectives. It involves a careful analysis of the learners’ needs, the content to be taught, and the context in which the learning will take place. By employing a systematic process, instructional designers ensure that the learning experience is well-structured, engaging, and optimized for learning outcomes.
The process of instructional design typically involves several stages. These stages may vary depending on the instructional design model being used, but they generally include the following:
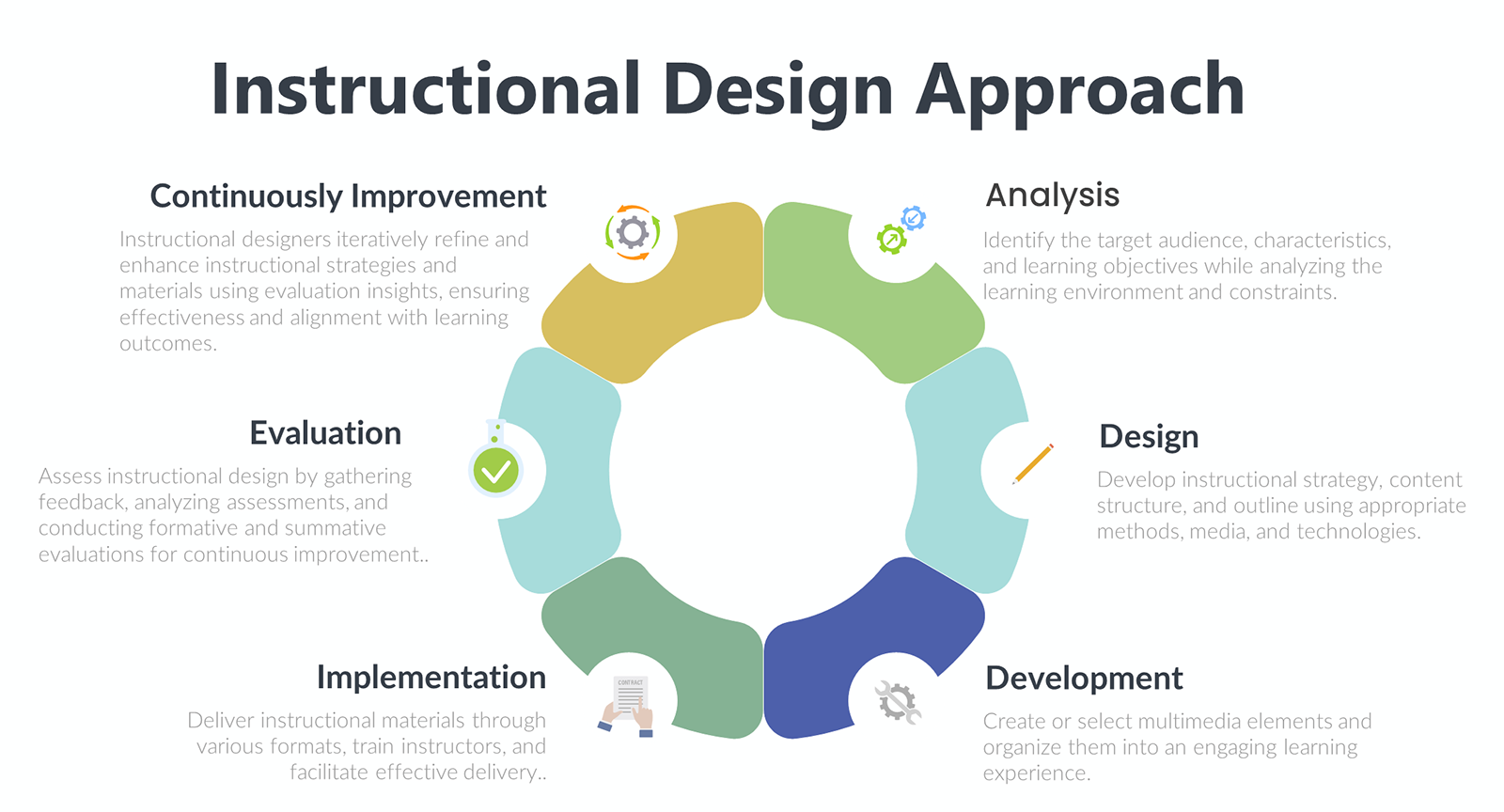
1.1 Analysis
In this initial phase, instructional designers identify the target audience and their characteristics, as well as the specific learning objectives. They also conduct a thorough analysis of the learning environment and any constraints or limitations that may impact the design.
1.2 Design
This stage focuses on developing the overall instructional strategy and content structure. Instructional designers determine the most appropriate instructional methods, media, and technologies to support the learning objectives. They also create a detailed outline or storyboard that outlines the sequence of content and activities.
1.3 Development
Once the design is finalized, the instructional materials are developed. This stage involves creating or selecting multimedia elements, such as text, images, videos, and interactive components. The materials are then organized and assembled into a cohesive and engaging learning experience.
1.4 Implementation
During the implementation phase, the instructional materials are delivered to the learners. This can take various forms, including classroom instruction, online courses, or blended learning approaches. Instructional designers may also train instructors or facilitators to ensure effective delivery of the materials.
1.5 Evaluation
The evaluation stage involves assessing the effectiveness of the instructional design. This may include gathering feedback from learners, analyzing assessment results, and conducting formative and summative evaluations. The insights gained from the evaluation process are used to refine and improve the instructional design for future iterations.
Instructional design plays a crucial role in creating meaningful and impactful learning experiences. By applying sound instructional design principles and techniques, educators and instructional designers can optimize the learning process and promote knowledge acquisition, retention, and application.
2. Instructional Design and Flipped Learning
When incorporating Flipped Learning 3.0 into instructional design, there are several necessary enhancements to consider. Flipped learning is an instructional approach that reverses the traditional order of content delivery and homework. Students are first exposed to instructional materials, such as videos or readings, outside the classroom, and then class time is dedicated to interactive activities, discussions, and the application of knowledge. To effectively integrate flipped learning, the following enhancements are recommended:
By incorporating these enhancements into instructional design, educators can effectively implement flipped learning. The combination of engaging pre-class materials, active learning strategies, technology integration, scaffolding and support, assessment alignment, and opportunities for reflection and metacognition creates a robust and learner-centered flipped learning experience.
3. About Flipped Learning 3.0
Flipped Learning 3.0 is an evolved approach to the flipped classroom model that emphasizes student agency and promotes more in-depth learning. It goes beyond simply flipping content delivery and focuses on fostering meaningful student-teacher interactions, personalized learning pathways, and the development of essential skills such as critical thinking, collaboration, and self-regulated learning. Flipped Learning 3.0 leverages technology and flexible learning environments to empower students to take ownership of their learning and encourages educators to become facilitators and mentors in the learning process. The two crucial pillars in Flipped learning 3.0 are the Individual Learning Space and the Group Learning Space.